Fusion Genesis Pte. Ltd. © 2020. Privacy Policy

WHAT IS IP SURVEILLANCE?
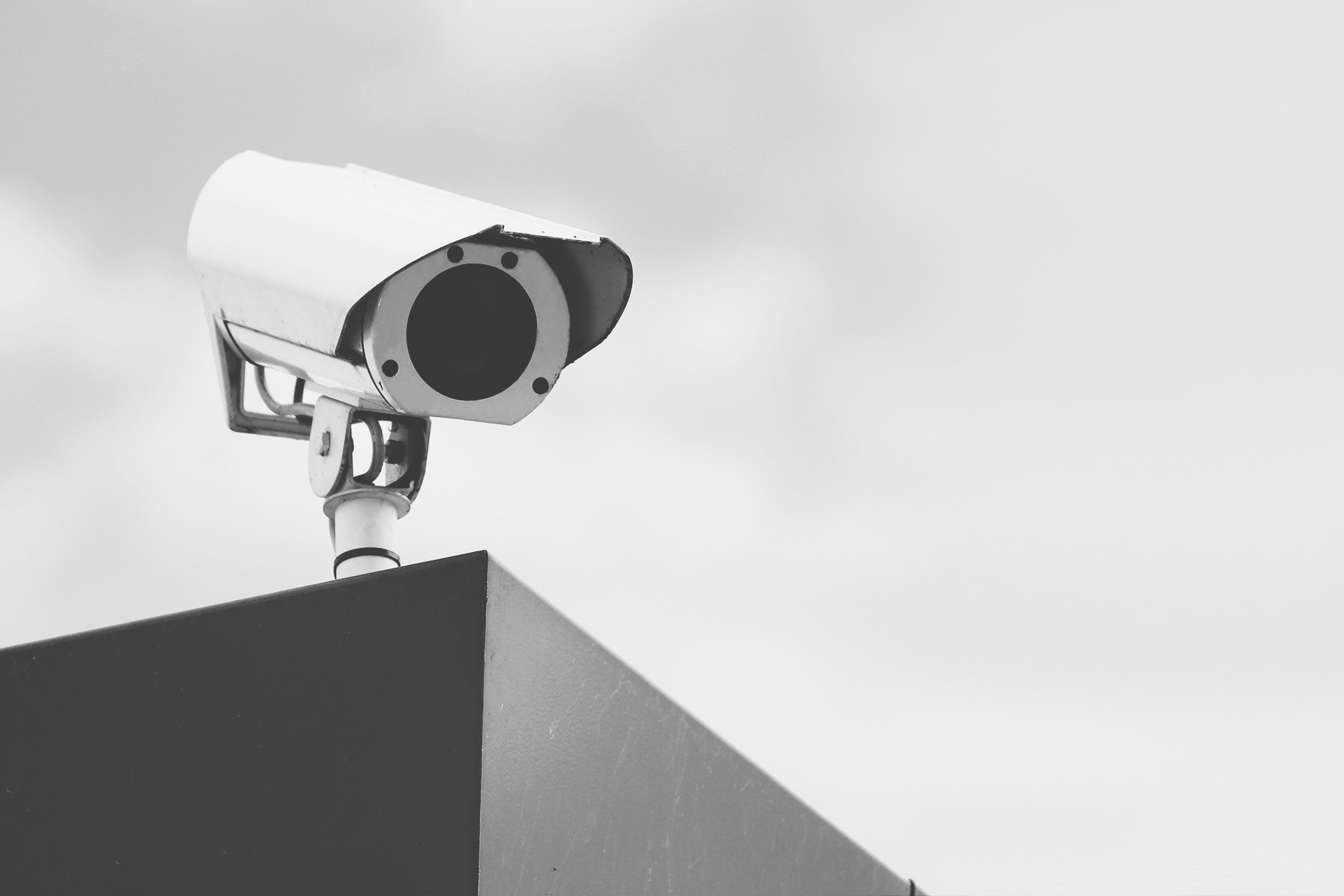
IP surveillance is a digitized and networked version of closed-circuit television (CCTV).
In an IP surveillance system, an IP camera records video footage and the resulting content is distributed over an IP (Internet protocol) network.




WHY IP SURVEILLANCE?
IP(Internet Protocol) is now the backbone of the global internet and nearly all data communications. Advances in computing power and network bandwidth have made it possible to compress and transmit digitised video streams over IP networks.
IP video surveillance is the game changer. So what are the advantages of an IP video surveillance system?
RESOURCES

REMOTE ACCESSIBILITY
With network video, users can access real-time video at any time from any authorised computer anywhere.
COST-EFFECTIVENESS
As it leverages IT infrastructure to reduce costs and improve scale, IP video is a cost-effective surveillance solution.
SCALABILITY & FLEXIBILITY
As security needs grow, IP video surveillance system offers scalability and flexibility that allow you to expand your network surveillance system. An IP camera can be added anywhere along the network, without the need for costly and fussy cabling.
BETTER VIDEO QUALITY
IP video provides high-quality video images and megapixel IP cameras are available to provide even more image details. Digital images are also more easily stored and retrievable.

GLOSSARY
This glossary contains a list of general terms and definitions related to surveillance systems
A
Angle of view
The maximum angle a camera can view through a lens
Aspect ratio
The ratio of the width of the picture to the height. A common aspect ratio used for television screens and computer monitors is 4:3. HDTV uses an aspect ratio of 16:9
AF (Autofocus)
A system where the camera lens automatically focuses on a selected part of the subject.
Automatic iris lens
A lens where the aperture automatically opens or closes to maintain proper light levels on the cameras pickup device. Also known as DC-Iris.
B
B.L.C. (Back Light Compensation)
A feature of modern CCD cameras which electronically compensates for high background lighting to give detail which would normally be silhouetted. A more advanced form would be WDR (Wide Dynamic Range).
Bandwidth
The amount of data allowed to your computer over a specific period of time, usually expressed in bits per second (bps).
C
C Mount / CS Mount
The two industry standards for mounting a lens on a camera. The C Mount lens has a 17.5mm flange back distance while the CS Mount lens has a 12.5mm flange back distance.
Camera
An device that translates light into a video image and transmits that image to a monitor for viewing. It contains the image sensor and other electronic circuitry to create a video signal.
CCD (Charged Coupled Device)
This light-sensitive image device used in many digital cameras is a large integrated circuit that contains hundreds of thousands of pixels that convert light energy into electronic signals.
D
Dynamic Noise Reduction (DNR)
A feature on a camera that reduces the static, or noise, on an image, especially under low light.
Dynamic IP Address
A Dynamic IP address is a type of account from an ISP (internet service provider) where your computer or network is assigned an IP address that constantly changing and never remains the same. Also see IP Address and Static IP.
F
Firewall
Acts as a barrier between networks, ensuring that only authorised users are allowed to access the one network from the other. It can be a software running on a computer or a standalone hardware device.
Fixed iris
In indoor environments where light levels are constant, a fixed iris lens can be used. The iris opening cannot be adjusted and is fixed at a certain f-number and the camera can compensate for changes in the level of light, if any, by adjusting the exposure time or using gain.
Focal length
Determines the width of the horizontal field of view of a camera lens.
FTP (File Transfer Protocol)
An application protocol that uses the TCP/IP protocols, used to exchange files between computers/devices on networks.
Frame rate
The frame rate used to describe the frequency at which a video stream is updated is measured in frame per second (fps). A higher frame rate is beneficial when there is movement in the video stream, as it maintains image quality throughout.
G
Gain
Gain is the amplification factor and the extent to which an analog amplifier boosts the strength of a signal. Amplification factors are usually expressed in terms of power. The decibel (dB) is the most common way of quantifying the gain of an amplifier.
I
IP Address
An IP address is simply an address on an IP network used by a computer/device connected to that network. IP addresses allow all the connected computers/devices to find each other and to pass data back and forth.
Infrared (IR) Illumination
When a “low-light” is subject to dark conditions, active infrared illumination must be applied for best results. Active infrared illumination is a new surveillance technology that is so effective that the images produced are often mistaken for regular daytime monochrome images. Active infrared illumination is a cost-effective technology for enabling truly effective 24/7 surveillance in any lighting conditions including total darkness.
L
LAN (Local Area Network)
A LAN is a group of computers and associated devices that typically share common resources within a limited geographical area.
License Plate Recognition (LPR)
Software that has the ability to read and store license plates on cars. It has the ability to count cars and when applied with a sensor, it can capture images of speeding cars or red-light violating cars.
Lux
A standard unit of illumination measurement.
M
MAC address
A MAC address is a unique identifier associated with a piece of networking equipment, or more specifically, its interface with the network. For example, the network card in a computer has its own MAC address.
Manual iris lens
A lens with a manual adjustment to set the iris opening (F stop) in a fixed position. Generally used for fixed lighting applications.
P
PTZ (Pan, Tilt, Zoom)
A versatile camera that has the ability to pan (move side-to-side), tilt (tilt up and down), and zoom (in and out) onto certain objects.
PoE (Power over Ethernet)
The transmission of power to a camera over an Ethernet cable, CAT5 generally.
S
Server
A computer program that provides services to other computer programs in the same or other computers. A computer running a server program is also frequently referred to as a server. In practice, the server may contain any number of server and client programs. A web server is the computer program that supplies the requested HTML pages or files to the client (browser).
Switch
A switch is a network device that connects network segments together, and which selects a path for sending a unit of data to its next destination. In general, a switch is a simpler and faster mechanism than a router, which requires knowledge about the network and how to determine the route. Some switches include the router function.
V
VPN (Virtual Private Network)
This creates a secure “tunnel” between the points within the VPN. Only devices with the correct "key" will be able to work within the VPN. The VPN network can be within a company LAN (Local Area Network), but different sites can also be connected over the Internet in a secure way. One common use for VPN is for connecting a remote computer to the corporate network, via e.g. a direct phone line or via the Internet.
Z
Zoom
The ability to change the magnification of a scene.
Zoom lens
A zoom lens can be moved (zoomed) to enlarge the view of an object to show more detail.